Code governance glossary
| Description | This document defines terminology and concepts of the code governance methodology. |
| Id | 127 |
| Last modified | Fri Jul 27 18:17:05 EDT 2007 |
| GUID | 4ffea34c999652b77199b73d6dcadcdb3415d79d |
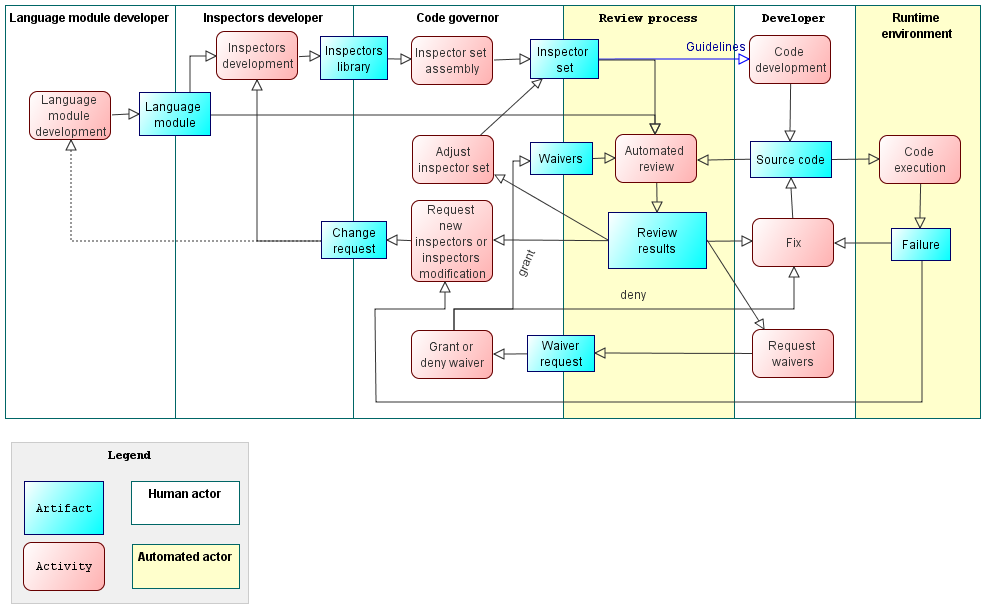 |
| Figure 1. Code governance process |
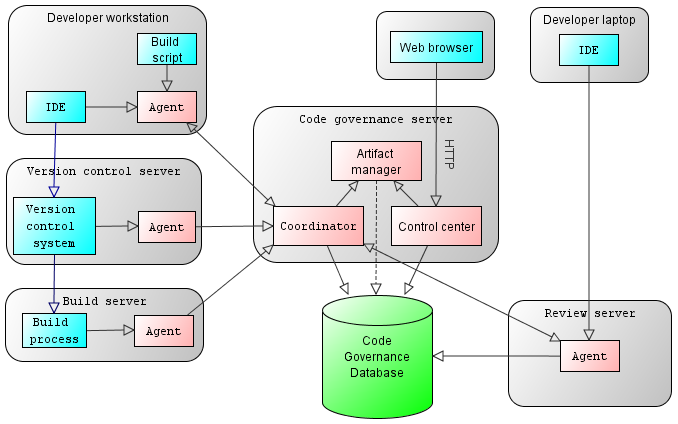 |
| Figure 2. Deployment architecture |
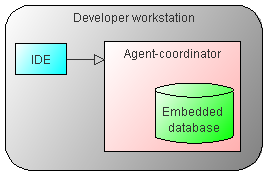 |
| Figure 3. Embedded embodiment |
Glossary
Actor
C
Code governor
Code governor is the central figure in the code governance process. Typically this role requires deep knowledge of target languages. Typically it is played by a senior developer or an architect.
D
Developer
Developers code application functionality. outsource, contractors, ...
I
Inspectors developer
Inspectors developer is responsible for development of
Term 284inspectors and registering them in the
Code Governance Control Center.
L
Language module developer
Language module developer is a person or organization responsible for development of
Term 271language modules and registering them in the
Code Governance Control Center.
R
Runtime environment
Environment where binaries build from sources produced by
Term 298Developer are executed to deliver business value.
Class
C
Code Governance Control Center
Component
Component is a collection of sources. It is unit of review. Component corresponds to
Term 274Repository and to a IDE 'Project'. A component belongs to one project, worked on by one or more developers.
I
Inspector
Inspector set
P
Product
Product is a collection of
Term 300components. ... Team allocation...
R
Review hook
A point in the
Term 296Development process at which sources are automatically reviewed. ... IDE, (local) build, version control
Component
A
Agent
Agent is a background process (e.g. Windows service), with the following responsibilities:
An agent can fulfill one, two or all three responsibilities at the same time.
Agent-oriented architecture has the following benefits:
- Minimal Term 263client configuration.
- Term 263Client can be written in any language - Java, .Net, C++, Ruby.
- Distributed processing, which is very important for large codebases.
Artifact manager
Artifact manager is responsible for storing uploaded
Term 305inspector libraries and assembling jar files stored in it into packages to support review with a particular
Inspector set. The artifact manager calculates SHA digests for each uploaded component and stores only unique artifacts. With the help of the Artifact Manager
Code Governance Control Center ensures that
inspector sets are assembled in a compatible way, e.g. it doesn't include
inspectors residing in different revisions of the same jar. Artifact manager is aware of internal structure of zip and jar files and introspects them to identify changes in inspector classes.
C
Client
Client is an application requesting to review source code. Clients communicate with
Term 262agents using XML over a variety of protocols, e.g. TCP/IP, HTTP, JMS.
Examples of clients:
- Plug-in for an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) performs background review of source files and displays results in the IDE problem window.
- Command-line tool scans a source directory, sends source files to the Term 262agent for review and prints review results to the console.
- A task for a build tool like Ant or make. The task sends source files to the Term 262agent for review, outputs review results to a file or console. It can also fail the build process if review results contain severe violations.
- A hook in the version control system can send source files being checked-in to review. Optionally the hook might disable checking-in of 'bad' code.
Code Governance Control center
Web application (-based) to manage code governance artifacts and processes and to access review results.
Code governance database
A relational database (or a set of databases) which stores configuration information, parsed sources, and review results.
Coordinator
Coordinator is an
Term 262Agent configured to coordinate code review process by distributing jobs to other
Term 262agents. There can be multiple coordinators in the network for load balancing purposes. Different algorithms can be employed to select review coordinator based on review initiating
Term 262agent. Several options are listed below:
- The Term 262Agent itself coordinates reviews, but delegates jobs to other agents when possible
- Each Term 262agent has an assigned coordinator.
- For each review Coordinator is chosen from a list of available coordinators using round-robin or other load balancing altgorithm.
Coordinator also serves as a remote classloader for
Term 262agents. Agents cache classes loaded from the
Coordinator. This approach obviates deployment of updates to each agent and also optimizes network utilization.
I
Inspector library
Inspector library contains jar file with
Term 284inspectors and helper classes, supporting jars, configuration files and documentation.
Operation
A
Automated review process
Automated review process is a process of parsing sources produced by
Term 298Developer(s), ...
B
Build process
Build process is a process of convertins sources produced by
Term 298Developer(s) into binary representation to...
D
Development process
...
References
Glossaries referenced by this glossary
